Several reasons for power transformer burnout:
1. Overvoltage
① Suffer from lightning strikes
The high and low voltage lines of power transformers are mostly introduced by overhead lines. Because they are located in mountainous forests, the probability of lightning strikes is high. Therefore, during the thunderstorm season every year, the proportion of distribution transformers damaged by lightning strikes accounts for over 30% of maintenance.
② The system has ferromagnetic resonance
Rural 10kV distribution lines have the conditions to form overvoltage. When the system experiences resonance overvoltage, the primary current of the transformer will experience surges. At this point, in addition to the fuse on the primary side of the transformer, the transformer winding will also be damaged. In individual cases, it can also cause flashover or explosion of transformer bushings.
2. Insulation damage
① The short circuit fault of low-voltage lines and the rapid increase in load make the current of transformers reach several tens of times the rated current. At this point, the winding is affected by a large electromagnetic torque and undergoes displacement deformation. Due to the rapid increase in current and temperature, insulation aging is accelerated.
② The winding insulation is damp. This is caused by poor insulation oil or low oil level. One is that during the storage, transportation, or operation and maintenance process of transformer insulation oil, moisture, impurities, or other oils are accidentally mixed into the oil, greatly reducing the insulation strength. The second reason is that the inner layer of the winding is not fully impregnated, dried thoroughly, and the winding lead joints are poorly soldered, resulting in incomplete insulation, resulting in inter turn and inter layer short circuits. Thirdly, the decrease in oil level increases the contact surface between insulation oil and air, accelerating the entry of moisture from the air into the oil will also reduce its insulation strength. When the insulation decreases to a certain value, a short circuit will occur.
3. Tap changer
① The transformer leaks oil, exposing the tap changer to the air. When the insulation is damp, the insulation performance decreases, causing short circuit discharge and damaging the transformer.
② The oil temperature is too high. The oil in transformers is mainly used for winding insulation, heat dissipation, and moisture prevention. If the oil temperature inside the transformer is too high, it will directly affect the normal operation and service life of the transformer.
③ The quality of the tap changer is poor, the structure is unreasonable, the pressure is insufficient, the contact is unreliable, and the position of the outer wheel is not completely consistent with the actual internal position, resulting in incomplete contact and displacement of the star moving contact. Static contacts. The insulation distance between two taps decreases, and a short circuit or ground discharge occurs under the potential between the two taps. Short circuit current can quickly burn out the tap turns and even damage the entire winding.
4. Oil seepage
Oil leakage is the most common appearance abnormality of transformers. Due to the transformer body being filled with oil, there are rubber beads and pads at each connection part to prevent leakage. After long-term operation of the transformer, the rubber beads and pads will age. Rupture and cause oil leakage. Of course, if the screws are loose or the drain valve is not tightly closed, bubbles or poor welding quality may occur during manufacturing, and oil leakage may also occur.
5. Multi point grounding of iron core
① The multi point grounding of the 10kV distribution transformer core is difficult to detect and test. This is because the iron core of the distribution transformer is internally grounded, with a thin layer of copper sandwiched between the iron core (silicon steel sheet) and the other end. It is pressed onto the iron core clamp and directly connected to the transformer casing.
② Short circuit between iron core silicon steel sheets. Although silicon steel sheets are coated with insulation paint, their insulation resistance is very small and can only block eddy currents, not high-voltage induced currents. If the insulation paint on the surface of the silicon steel sheet naturally ages, it will generate significant eddy current loss and increase local overheating of the iron core. ł
6. Overload
① The uneven distribution of three-phase load in distribution transformers leads to three-phase current asymmetry, which leads to a decrease in transformer impedance and an imbalance in low-voltage three-phase voltage, which is not conducive to transformers and users' electrical equipment.
② When the low-voltage side of the transformer is grounded and there is a short circuit between phases, a short circuit current 20 to 30 times higher than the rated current will be generated. The action of such a large current on the high-voltage winding will generate significant mechanical stress inside the coil. Mechanical stress will compress the coil, and the stress will disappear after the short circuit fault is eliminated. If the coil is repeatedly subjected to mechanical stress, its insulation gasket, pad, etc. will become loose and fall off; The iron core clamp screws will also loosen, and the high-voltage coil will deform or break. In addition, it will generate temperatures several times higher than the allowable temperature rise, causing the transformer to burn out in a short period of time.
7. Artificial damage
① The outgoing line of the transformer is copper wire, and the overhead line generally uses aluminum core rubber wire, which is prone to electrochemical corrosion between copper and aluminum. Under ionization, an oxide film is formed between copper and aluminum, increasing contact resistance., Burn or fuse the screws, nuts, and leads at the location of the leads.
② Bushing flashover discharge is also one of the common appearance abnormalities in transformers. Conductive metal dust in the air adheres to the surface of the casing. If encountering rainy, snowy, and humid weather, the power grid system will experience resonance, lightning strikes, and overvoltage, which will cause flashover discharge or explosion of the bushing.
③ During the process of tightening or loosening the lead nut of the transformer, the conductive screw rotates, causing the high-voltage coil lead inside the transformer to twist or the soft copper strip from the low-voltage to collide, resulting in a circuit between the short circuited phases.
④ During the overhaul of the lifting iron core, the maintenance procedures and process standards are not followed, and the insulation of the coil, lead wire, tap changer, etc. is often accidentally damaged, or the tools inside the transformer, lights flash, or short circuited to the ground are forgotten.

Prevention methods:
① Regularly check whether the three-phase current is balanced or exceeds the rated value. If the three-phase load current is severely unbalanced, measures should be taken to adjust it in a timely manner; Check if the oil level of the transformer is normal and if there are any leaks. If found, replenish the oil as soon as possible to avoid lightly tapping the switch and coil from being exposed to moisture in the air.
② Regularly clean the dirt on the surface of the distribution transformer casing: check whether the casing has flashover marks, whether the grounding is good, and whether the grounding wire has broken strands, desoldering, or wires; The grounding resistance should not exceed 4 Ω, and a grounding resistance tester should be used.
③ Reasonably choose the wiring method for low-voltage side conductors, such as copper aluminum transition clamps or terminal blocks. And apply conductive paste on the contact surface to increase the contact area and prevent heating and oxidation.
④ According to the technical requirements of 10/0.4kV distribution transformers, install a set of lightning arresters near the high and low voltage sides of the transformer.
⑤ When switching the tap changer, it is necessary to use a bridge to measure the DC resistance values of the first two times and make records. Compare whether the three-phase DC resistance is balanced (with a phase difference of no more than 4% and a line difference of no more than 2%), compare the DC resistance values after switching with the records before switching, and confirm that the switching is normal before putting them into operation.
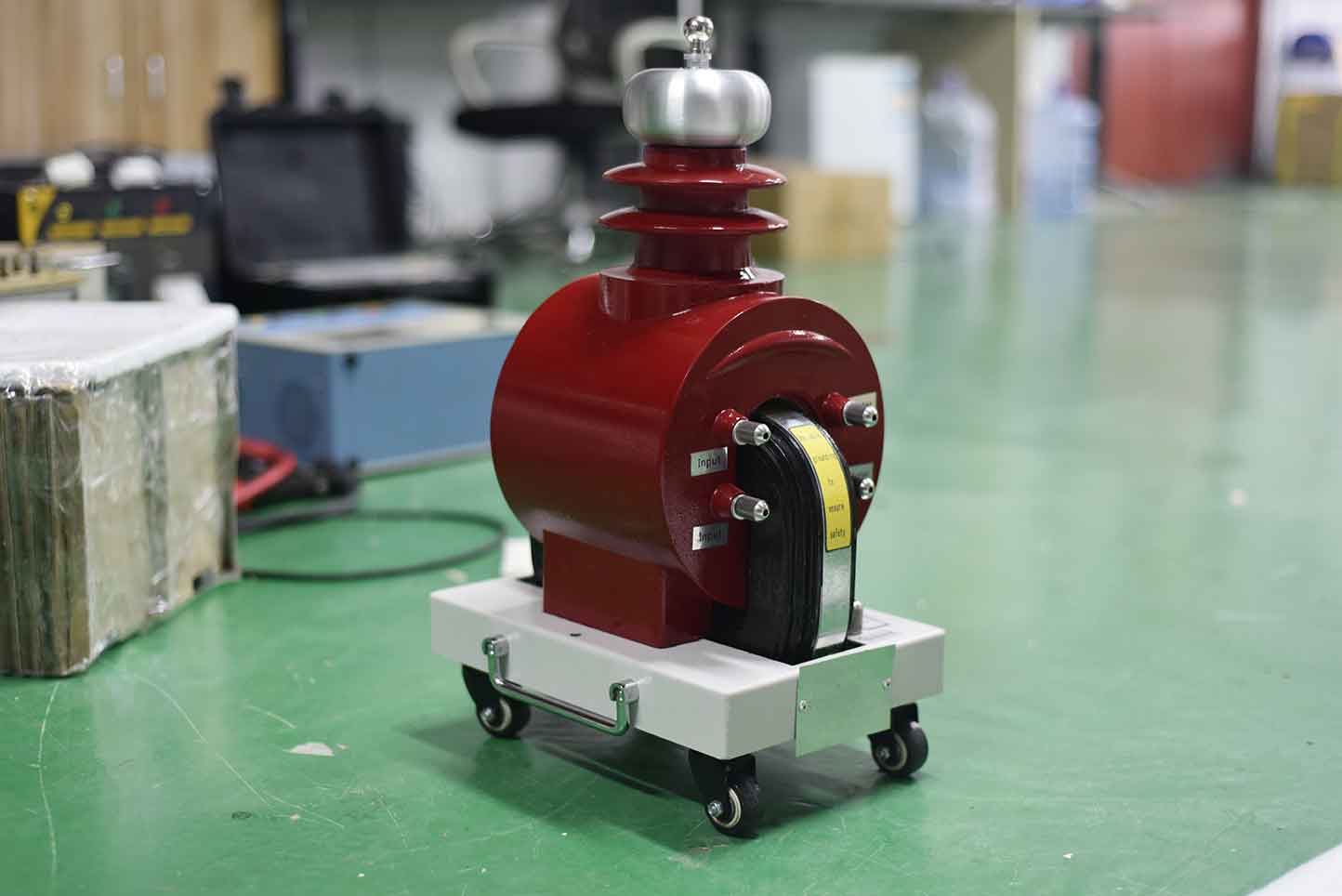
The ZC-501C series dry type test transformer has the characteristics of light weight, small size, beautiful appearance, stable performance, and convenient use and portability. It is particularly suitable for on-site operation and is a new generation of AC DC dual purpose high-voltage test transformer in China. This series of dry test transformers is suitable for on-site insulation performance testing of various electrical equipment in power systems and power users, as well as for high-voltage power supply in various voltage systems or devices with DC high voltage and small current of electrical products.
Kvtester Electronics Technology Co.,Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise specializing in power testing, testing, research and development, production, and sales of testing equipment. It has been engaged in the electrical testing industry for many years, and its products are of high quality. We welcome customers to come and purchase.