The insulation absorption ratio and polarization index are important indicators for evaluating the insulation performance of electrical equipment. Both reflect the insulation state by measuring the change in insulation resistance over time, but there are significant differences in test time, applicable scenarios, and diagnostic significance. The following is a detailed comparative analysis:
1. Definitions and Test Methods
① Insulation Absorption Ratio
a. Definition: The ratio of the insulation resistance value measured at 60 seconds (R₆₀) to the insulation resistance value measured at 15 seconds (R₁₅), i.e., K = R₆₀ / R₁₅.
b. Test Method: Apply a DC voltage (e.g., 500V) to the insulation using a megohmmeter (e.g., 500V, 1000V, 2500V). Record the insulation resistance values at 15 seconds and 60 seconds, and calculate the ratio.
c. Physical Significance: Reflects the polarization process of the insulating material in a short time (within 1 minute), i.e., the speed of charge redistribution in the insulating medium.
② Polarization Index
a. Definition: The ratio of the insulation resistance value measured at 10 minutes (R₁₀) to the insulation resistance value measured at 1 minute (R₁), i.e., PI = R₁₀ / R₁.
b. Test Method: Similarly, apply a DC voltage using a megohmmeter. Record the insulation resistance values at 1 minute and 10 minutes, and calculate the ratio.
c. Physical Significance: Reflects the polarization process of the insulating material over a longer period (10 minutes), focusing more on evaluating the long-term stability and moisture content of the insulation.
2. Core Differences Comparison
| Dimension | Insulation Absorption Ratio (K) | Polarization Index (PI) |
| Test Duration | 15 seconds vs. 60 seconds (short duration) | 1 minute vs. 10 minutes (long duration) |
| Applicable Voltage Levels | Low-voltage equipment (e.g., motors, switchgear) | High-voltage equipment (e.g., transformers, cables, generators) |
| Diagnostic focus | Surface contamination and localized moisture of insulation | Overall aging, deep-seated moisture, or degradation of insulation |
| Sensitivity | Sensitive to surface defects | Sensitive to deep defects |
| Standard Thresholds | Generally requires K ≥ 1.3 (some standards require 1.6) | Generally requires PI ≥ 2.0 (some standards require 1.5) |
| Testing Efficiency | Fast (completed in 1 minute) | Time-consuming (completed in 10 minutes) |
3. Application Scenarios and Selection Criteria
① Prioritize Insulation Absorption Ratio (K):
a. Low-voltage equipment: such as electric motors, low-voltage cables, control cabinets, etc., due to short testing time and high efficiency.
b. Preliminary screening: Quickly determine if there are obvious insulation defects (such as surface contamination, slight dampness).
c. On-site testing: Used in situations where space is limited or time is tight.
② Prioritize Polarization Index (PI):
a. High-voltage equipment: such as transformers, high-voltage cables, generators, etc., due to large insulation thickness and slow polarization process.
b. In-depth diagnosis: Detect aging, deep moisture, or chemical degradation of insulation materials (such as carbonization of oil-impregnated paper insulation).
c. Preventive testing: As part of regular maintenance, assess the long-term reliability of the insulation.
③ Combined Use:
a. For important equipment (such as large transformers), both K and PI can be measured simultaneously for a comprehensive analysis of the insulation condition.
b. If the K value is close to the threshold but the PI value is normal, it may indicate a surface problem; if the PI value is low but the K value is normal, attention should be paid to deep-seated defects.
4. Result Interpretation and Precautions
① Result Interpretation:
a. K value:
K ≥ 1.3: Good insulation.
1.0 < K < 1.3: Insulation is suspect, further inspection is required.
K ≤ 1.0: Insulation is severely damp or deteriorated.
b. PI value:
PI ≥ 2.0: Good insulation.
1.5 ≤ PI < 2.0: Insulation is suspect, monitoring or drying treatment is required.
PI < 1.5: Insulation is unqualified, repair or replacement is required.
② Precautions:
Temperature influence: Insulation resistance decreases with increasing temperature; results should be corrected to a standard temperature (e.g., 20℃) for comparison.
Humidity influence: Test results may be lower in high humidity environments; retesting should be performed under dry conditions.
Equipment type: Thresholds may vary for different types of equipment (e.g., oil-immersed, dry-type); refer to the manufacturer's recommendations.
Historical data: Comparing with historical test results of the equipment provides a more reliable trend analysis.
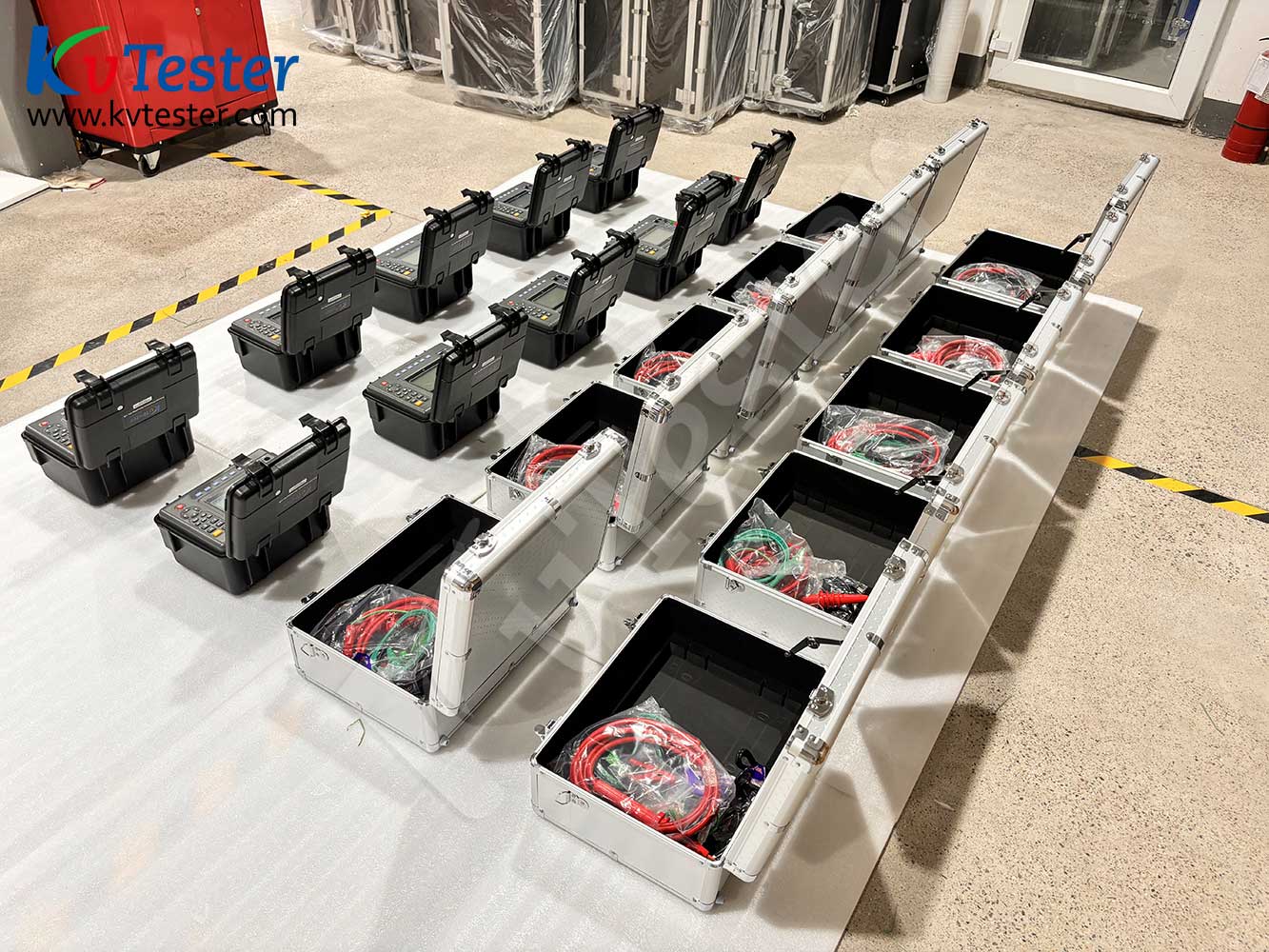

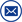
ZC-430C Digital insulation resistance meter also known as megohmmeter, high voltage insulation resistance tester, etc., for the insulation resistance test. The instrument has a large LCD screen gray backlit display, data storage, data access, alarm, automatic shutdown and other functions. At the same time, it also has the function of measuring DC voltage, AC voltage, absorption ratio and polarization index of DC voltage. It is suitable for measuring the resistance value of various insulating materials and the insulation resistance of transformers, motors, cables and electrical equipment.At the same time, it can output a variety of different voltage levels with the step-adjusting voltage function.
Kvtester Electronics Technology Co.,Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise specializing in power testing, testing, research and development, production, and sales of testing equipment. It has been engaged in the electrical testing industry for many years, and its products are of high quality. We welcome customers to come and purchase. Service hotline: 0086-27-81778799, to learn more, visit the official website: www.kvtester.com