There are significant differences between current transformers and voltage transformers in multiple aspects. The following is a detailed comparative analysis:
1. Convert objects differently
① Current transformer: mainly used to convert high current into low current for measuring and protecting equipment. It is commonly used in current measurement, energy metering, relay protection, and automatic control.
② Voltage transformer: mainly used to convert high voltage into low voltage for measuring and protecting equipment. It is commonly used in voltage measurement, energy metering, relay protection, and automatic control.
2. Differences in structure and working principle
① Current Transformer:
Structure: Typically composed of a circular iron core and one or more windings.
Working principle: Based on the principle of electromagnetic induction, when a large current passes through the primary winding (main circuit), a corresponding induced current will be generated in the secondary winding (measuring circuit). The primary winding of a current transformer has more turns, while the secondary winding has fewer turns, in order to achieve the conversion between high and low currents.
② Voltage Transformer:
Structure: Usually composed of one winding and one iron core.
Working principle: Based on the principle of electromagnetic induction, when a high voltage is passed through the primary winding (high voltage side), a corresponding induced voltage will be generated in the secondary winding (low voltage side). The primary winding of a voltage transformer has fewer turns, while the secondary winding has more turns, in order to achieve the conversion between high and low voltage.
3. Performance characteristics and application scenarios
① Current Transformer:
Performance characteristics: Wide current range, capable of handling currents from a few amperes to tens of thousands of amperes; Strong short-circuit withstand capacity, the impact of short-circuit current needs to be considered in design; They have a larger capacity because they need to carry high currents.
Application scenario: Mainly used for current measurement and protection in power systems, it can also be used to measure the unbalanced current of parallel capacitor banks and achieve balance control of parallel capacitor banks; It also has certain applications in fields such as direct current transmission and power electronics.
② Voltage Transformer:
Performance characteristics: High insulation requirements due to direct contact with high voltage; High accuracy requirements, requiring accurate voltage measurement values to be provided; The capacity is small because they do not need to carry large currents.
Application scenarios: Mainly used for voltage measurement and protection in power systems, as well as controlling voltage levels in automatic control systems.
4. Secondary side load and grounding requirements
① Current Transformer:
Secondary side loads: can be larger as they require driving more measurement and protection equipment.
Grounding requirement: The secondary circuit must be grounded to prevent high voltage from entering the secondary circuit during insulation breakdown, which may threaten personal safety and damage equipment.
② Voltage Transformer:
Secondary side load: usually small.
Grounding requirements: There are no specific grounding requirements, but it should be ensured that the secondary side is not short circuited.
5. Other precautions
① Current transformer: Open circuit is not allowed in the secondary circuit. When the current transformer is open circuited, the impedance of the secondary circuit is infinitely large, the current is zero, and the primary current completely becomes the excitation current, generating a high potential in the secondary winding, threatening personal safety and causing damage to the secondary insulation of the instrument and transformer.
② Voltage transformer: The secondary side can be open circuited, but it must not be short circuited. If the secondary side of the voltage transformer is short circuited, it will cause a sharp increase in current, which may damage the transformer or cause safety accidents.
In summary, there are significant differences between current transformers and voltage transformers in terms of conversion objects, structures, working principles, performance characteristics, application scenarios, as well as secondary side load and grounding requirements. In practical applications, the appropriate type of transformer should be selected based on specific needs and the characteristics of the power system.
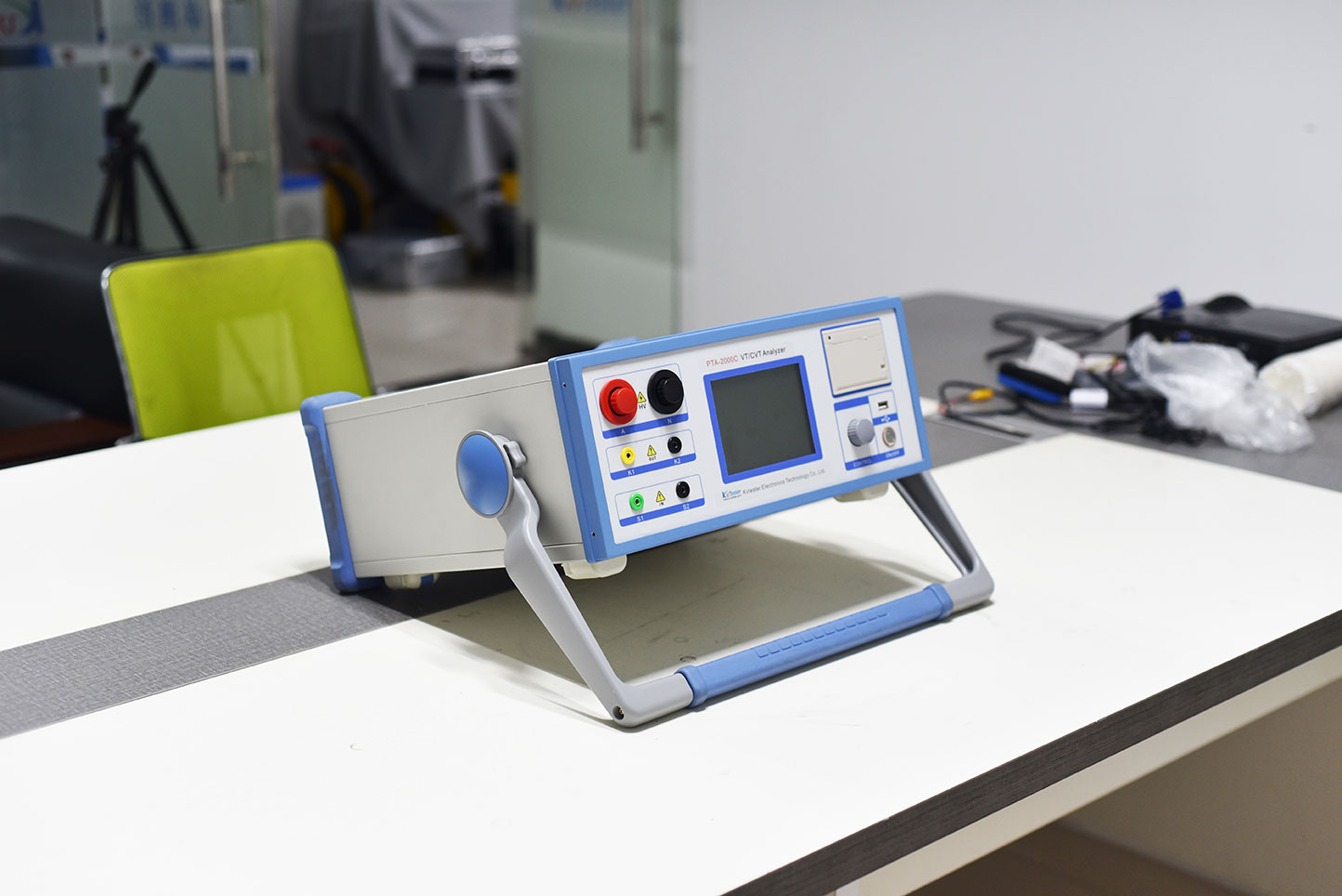

PTA-2000C Capacitive Voltage Transformer Tester, also known as Capacitive Voltage Transformer Field Tester or Capacitive PT Field Calibration Instrument, is mainly used to test the characteristics and errors of Capacitive Voltage Transformer PT (CVT) and Electromagnetic Voltage Transformer PT.
Kvtester Electronics Technology Co.,Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise specializing in power testing, testing, research and development, production, and sales of testing equipment. It has been engaged in the electrical testing industry for many years, and its products are of high quality. We welcome customers to come and purchase. Service hotline: 0086-27-81778799, to learn more, visit the official website: www.kvtester.com