Cable fault tester is a key equipment used in industries such as power, communication, railway, and petrochemical to detect and locate cable faults. It has a wide range of applications, covering various cable types and fault scenarios, as follows:
1. Applicable cable types
① Power cable
Voltage level: Low voltage (below 1kV), medium voltage (1kV-35kV), high voltage (above 35kV) cables.
Insulation materials: cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), oil impregnated paper insulation, rubber insulation, etc.
Application scenarios: urban power grids, substations, factory distribution systems, etc.
② Communication cable
Types: Symmetric cable (such as audio cable), coaxial cable, fiber optic composite cable (such as ADSS, OPGW).
Application scenarios: telecommunications networks, broadcasting and television, data transmission, etc.
③ Railway Signal and Power Cable
Signal cable: used for railway signal transmission, such as track circuit cables.
Power cables: used in railway power supply systems, such as overhead contact line feeders and substation cables.
④ Petrochemical and mining cables
High temperature and corrosion-resistant cables: used in high temperature, humid, and corrosive environments such as mines and chemical plants.
2. Applicable fault types
① Low resistance fault
Feature: The resistance at the fault point is less than 10 times the characteristic impedance of the cable (such as short circuit, grounding).
Detection methods: Low voltage pulse reflection method, electric bridge method.
② High resistance fault
Characteristic: The resistance at the fault point is higher than 10 times the characteristic impedance of the cable (such as insulation aging and breakdown).
Detection methods: high-voltage flashover method (direct flashover, impulse flashover), secondary pulse method.
③ Wire breakage fault
Feature: Cable conductor breakage, resulting in an open circuit.
Detection methods: Low voltage pulse reflection method, time-domain reflection method (TDR).
④ Flashover fault
Feature: The fault point breaks down instantly under high voltage, and the insulation is restored after the voltage drops.
Detection methods: high-voltage flashover method, pulse current method.
⑤ Comprehensive malfunction
Feature: There are multiple types of faults present simultaneously (such as high resistance grounding+disconnection).
Detection method: Combining multiple testing techniques.
3. Applicable scenarios and industries
① Power industry
Application: Cable fault location in urban power grids, power plants, and substations.
Case: A power grid cable in a certain city was short circuited due to construction damage, and the high-voltage flashover method was used to quickly locate the fault point.
② Communication industry
Application: Cable fault detection in telecommunications networks, broadcasting and television, and data centers.
Case: A communication cable in a data center experienced signal interruption due to lightning strikes, and the location of the disconnection was located using TDR technology.
③ Railway industry
Application: Fault detection of railway signal cables and contact network feeders.
Case: A railway signal cable experienced signal loss due to aging, and the secondary pulse method was used to locate the fault point.
④ Petrochemical and Mining
Application: Fault detection of mine cables and high-temperature cables in chemical plants.
Case: The insulation of a chemical plant cable was reduced due to corrosion, and the fault point was located through high resistance fault testing.
4. Other applicable scope
① Cable path detection
Function: Use electromagnetic induction or radar methods to locate the cable burial path.
Application: Detection of underground cables in cities and cable paths along railways.
Cable length and attenuation test
Function: Measure parameters such as cable length and signal attenuation.
Application: Cable quality inspection, communication system maintenance.
② Cable identification
Function: Identify target cables among multiple cables.
Application: Maintenance and management of complex cable networks.
5. Technical advantages
High precision positioning: can accurately locate fault points up to the meter level.
Multi functional integration: integrating path detection, fault location, and length measurement.
Safe and reliable: Supports high-voltage flashover testing to ensure the safety of operators.
Portability: Some devices are small in size and light in weight, making them suitable for on-site operations.
6. Summary
The cable fault tester is suitable for fault detection and location of various power, communication, railway, and petrochemical cables, covering multiple types of faults such as low resistance, high resistance, wire breakage, and flashover. By selecting appropriate testing methods (such as low voltage pulse, high voltage flashover, secondary pulse, etc.), cable faults can be efficiently resolved to ensure the safe operation of the system.
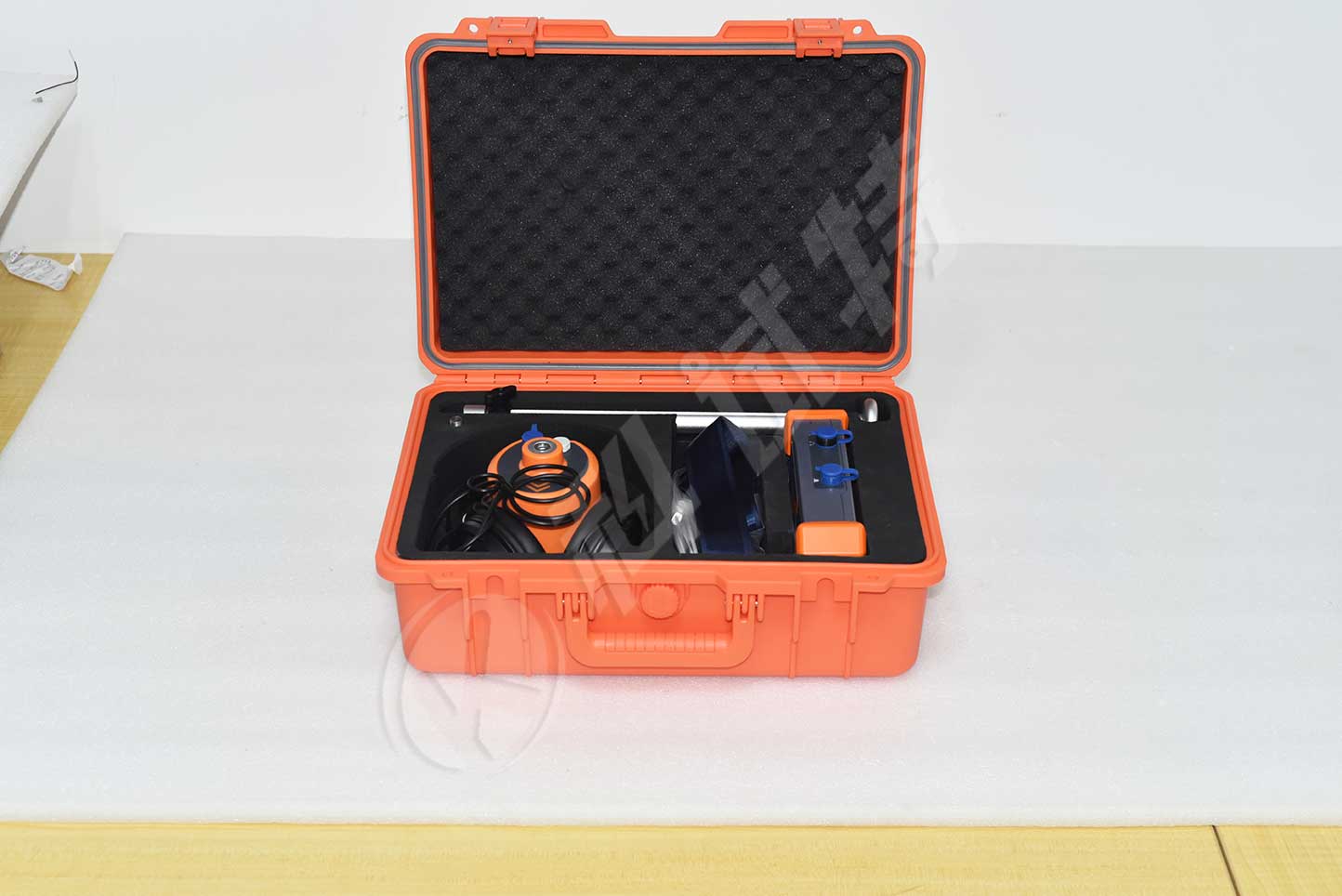

ZC-705DN Cable fault locator is an easy operation device used to pinpoint the fault point. It integrated the function of acoustic magnetic synchronization method, the step voltage method, the magnetic field strength method to make the pinpointing accuracy.
Kvtester Electronics Technology Co.,Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise specializing in power testing, testing, research and development, production, and sales of testing equipment. It has been engaged in the electrical testing industry for many years, and its products are of high quality. We welcome customers to come and purchase. Service hotline: 0086-27-81778799, to learn more, visit the official website: www.kvtester.com