1、 The reasons for the increase in no-load loss and no-load current of transformers include:
① Poor insulation between silicon steel sheets.
② There is a short circuit between a certain part of the silicon steel sheet in the magnetic circuit.
③ The insulation of the core bolts or pressure plates, upper yoke iron, and other parts is damaged, resulting in a short circuit.
④ The looseness of the silicon steel sheet in the magnetic circuit leads to an air gap, which increases the magnetic resistance.
⑤ The coil has a short circuit between turns or in parallel.
⑥The number of coil turns in each parallel branch is different.

2、 What are the reasons for high transformer losses?
Transformer loss is a concept in the field of Modern physics, which refers to the sum of no-load loss P and short-circuit loss Pk.
No-load loss P: When the rated voltage is applied to one winding of a transformer while the other windings are open, the active power absorbed by the transformer is called no-load loss.
Short circuit loss Pk: For a dual winding transformer, the active power absorbed by the transformer when passing through one winding at rated current and the other winding is shorted is called the short circuit loss of the transformer. For multi winding transformers, short-circuit losses are based on the specified pair of windings.
3、 There are two main reasons for transformer losses:
① When winding transformers, a large amount of copper wire is required, which has resistance. When current flows through the resistance, it consumes a certain amount of power, which is often converted into heat and consumed. This loss is called "copper loss".
② When the primary winding of the transformer is energized, the magnetic flux generated by the coil flows through the iron core. The iron core itself is also a conductor, and an electric potential is induced in a plane perpendicular to the magnetic field line. This electric potential forms a closed circuit on the cross-section of the iron core and generates current, known as "eddy current". This' eddy current 'increases the loss of the transformer, causing the iron core of the transformer to heat up and increasing the temperature rise of the transformer. The loss caused by "eddy current" is called "iron loss". The temperature rise of transformers is mainly caused by iron and copper losses. Due to the existence of iron and copper losses in transformers, the output power is always lower than the input power.
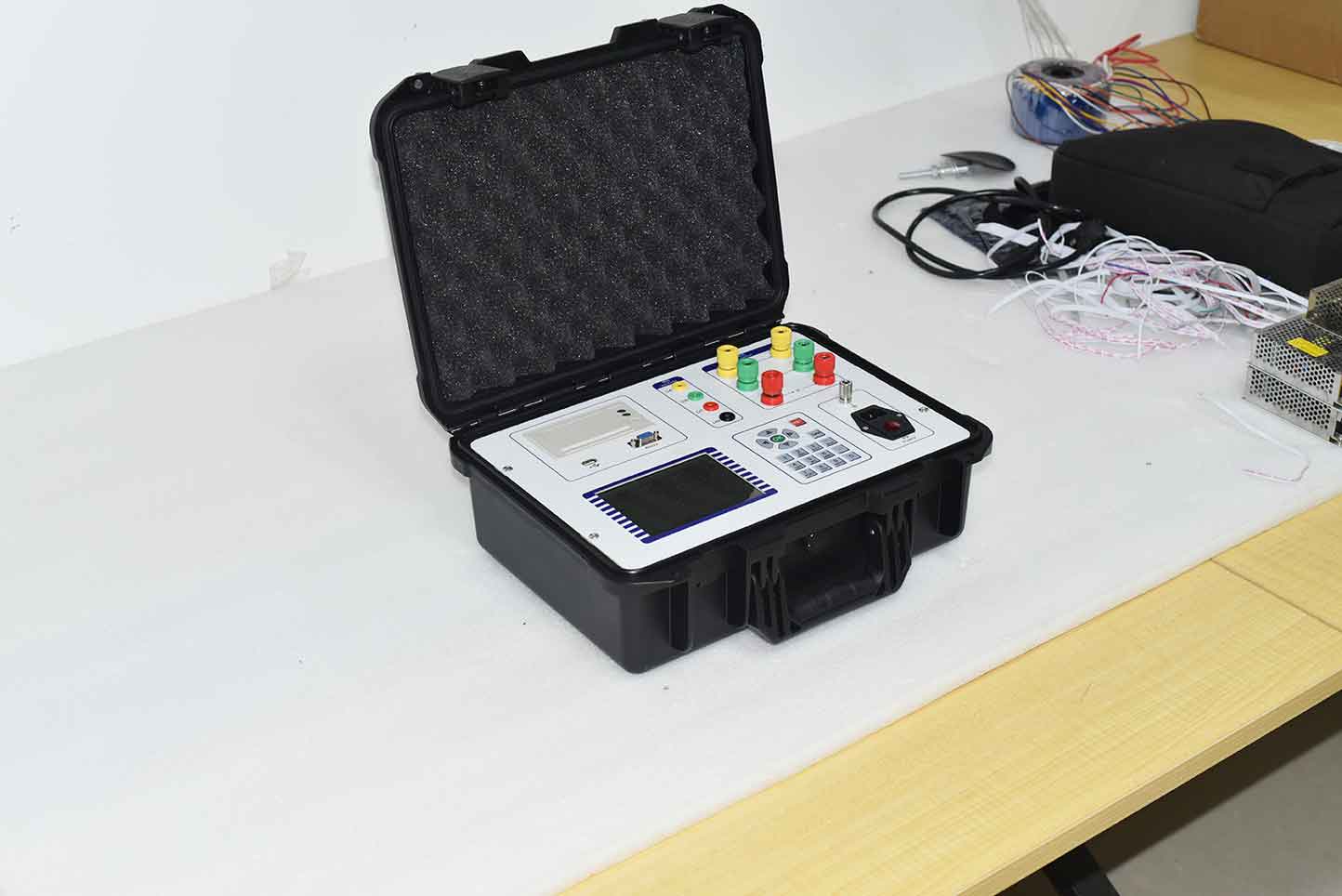

The ZC-202A transformer no-load load comprehensive characteristic tester can measure the no-load current, no-load loss, short-circuit voltage, and short-circuit (load) loss of the transformer. Harmonic testing can be conducted to analyze up to 31 harmonics. The instrument automatically switches range internally, allowing for a wide range of voltage and current measurements, and simple wiring. When conducting no-load and load tests on three-phase transformers, the instrument can automatically judge whether the wiring is correct and display the vector diagram of three-phase voltage and current.
Kvtester Electronics Technology Co.,Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise specializing in power testing, testing, research and development, production, and sales of testing equipment. It has been engaged in the electrical testing industry for many years, and its products are of high quality. We welcome customers to come and purchase.