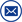
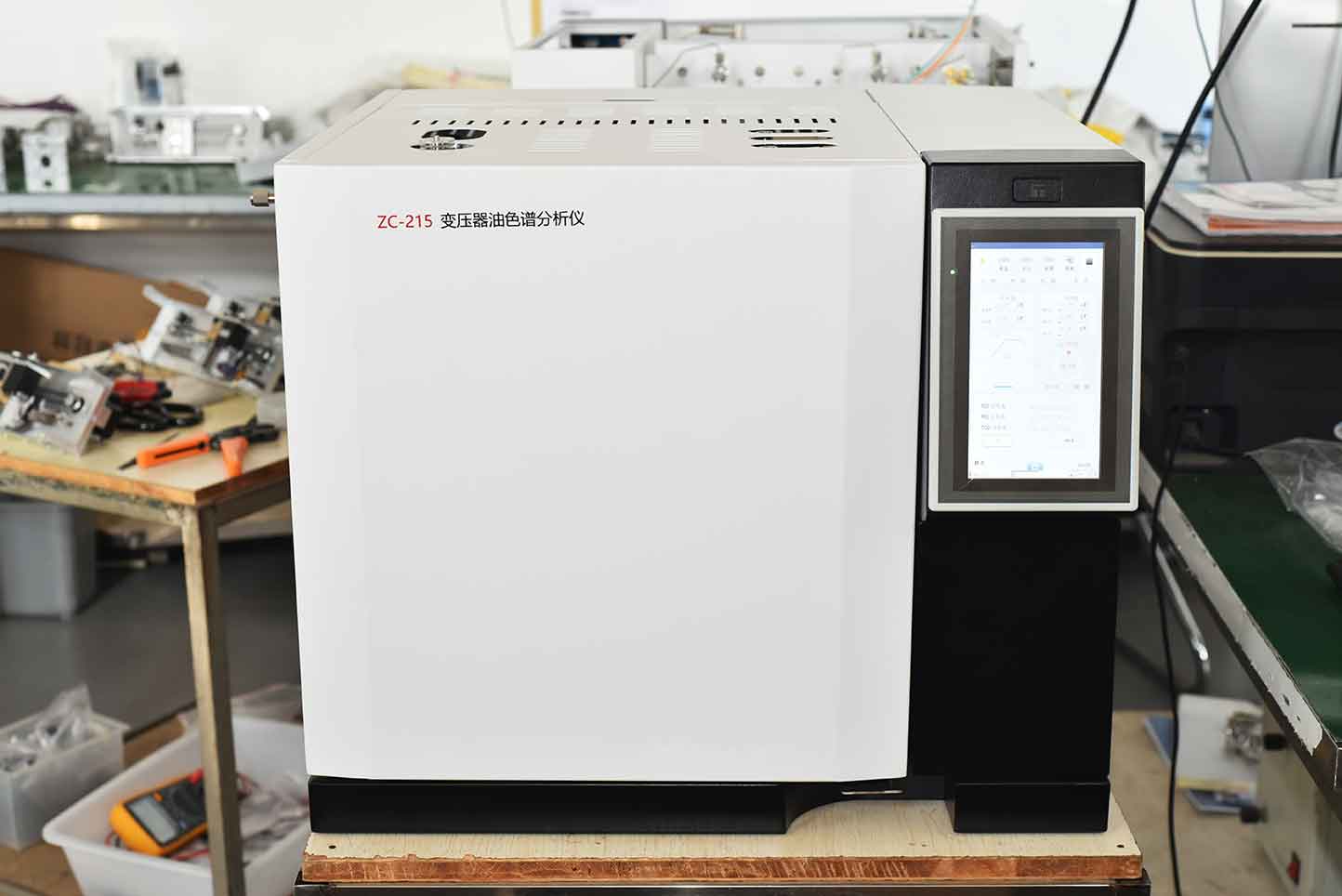
The oil chromatography analyzer mainly utilizes the differences in boiling point, polarity, and adsorption properties of substances to achieve the separation of mixtures. After the sample to be analyzed vaporizes in the gasification chamber, an inert gas (i.e. carrier gas, also known as mobile phase) is introduced into the chromatographic column. This column contains a liquid or solid stationary phase. The components in the sample tend to be in the mobile phase, forming a distribution or adsorption equilibrium between the fixed phases. As the carrier gas flows, the sample components are repeatedly distributed or adsorbed/desorbed during the movement process. The components with high concentrations in the carrier gas first flow out of the chromatographic column, and the components with high concentrations are distributed in the stationary phase. After discharge. After the component flows out of the chromatographic column, it enters the detector for determination.
How to improve the sensitivity of gas chromatography without increasing sample concentration?
Sensitivity "refers to the magnitude of the electrical signal (voltage: mV, current: mA) generated when a certain amount of component passes through the detector. Improving instrument sensitivity is an eternal topic in analytical chemistry. As for oil chromatography analyzers, instrument manufacturers and analysts always attempt to manufacture highly sensitive instruments and develop highly sensitive methods. It is precisely this demand that has driven the development of instruments, which has led regulatory manufacturers to demand higher detection sensitivity. This interaction is cyclical. So how to improve sensitivity without increasing sample concentration?
The reasons for reduced sensitivity may include:
1. Using shunt injection.
2. The sample did not fully enter the chromatographic column.
3. The instrument is contaminated, especially at the injection port and chromatographic column, resulting in increased system noise and masking the response of the compound.
4. Compounds are easily adsorbed by active sites at the injection port, exhibiting matrix effects.
5. The sensitivity of the selected detector has decreased.

Several methods to improve detection sensitivity:
① Non split injection:
The so-called non split injection refers to closing the solenoid valve of the split gas circuit during injection, allowing all samples to be injected into the chromatographic column. This can improve sensitivity and eliminate transfer discrimination. The sensitivity of non split injection is significantly higher than that of split injection, but the background signal also increases. Usually used for environmental analysis (such as monitoring trace pollutants in water and air), pesticide residue detection in food, and clinical and pharmaceutical analysis.
② Choose a detector with high specificity and sensitivity:
This is also a common method for chromatographic workers to improve sensitivity. For example, ECD is used to analyze halogenated compounds, NPD is used to analyze nitrogen and phosphorus compounds, and FPD is used to analyze sulfur and phosphorus compounds. Of course, universal detectors with higher sensitivity such as mass spectrometry detectors (MSD) can also be used.
③ Maintain instruments to reduce system noise:
Instrument system noise usually comes from two aspects: one is the instrument itself, such as detector noise, circuit noise, fixed phase loss, etc; Another type is the sample matrix, where the injection solution contains many impurities and picking up high background noise may cause contamination of the injection port and chromatographic column system. The former can be suppressed by using selective detectors and low loss chromatographic columns; The latter requires purification of the sample, such as solid phase extraction (SPE) or other methods to eliminate sample matrix interference, and timely replacement of the liner, cleaning of the system, etc.
④ Using a deactivated liner at the injection port:
The active sites on the liner may adsorb the components to be tested, causing tailing of chromatographic peaks, reducing sensitivity, and affecting reproducibility. The use of inert, low loss, and thermally stable deactivation liners can typically significantly improve the sensitivity of active substances when analyzing weakly polar compounds without splitting the sample, which has been difficult to solve in previous analyses. Suitable for the analysis of complex matrices and active substances.
⑤ Using a chromatographic column with no pollution and low loss of fixative: The chromatographic column has been used for a long time, causing severe loss of fixative, resulting in the exposed carrier adsorbing the sample. Some carriers are becoming more and more abundant, and due to the presence of their active sites, the analyzed components will directly contact the surface of the carrier during the analysis process, resulting in adsorption. At the same time, the loss of stationary phase will increase the chromatographic baseline, thereby reducing sensitivity.
⑥ Using a matrix to prepare a standard solution to improve sensitivity:
In GC analysis, matrix effects are often encountered, which seriously affect the accuracy and precision of the results. For example, organic phosphorus pesticides with smaller molecular weights are more susceptible to matrix influence, exhibiting matrix enhancing effects. Due to the presence of the matrix, the active sites on the injection port liner and chromatographic column are covered, reducing the number of active sites and the substance to be tested. The opportunity for exposure enhances the signal of the substance to be tested. Therefore, it is advisable to use matrix extracts with the same composition as the sample solution as the diluent of the compound as much as possible to improve the sensitivity of the tested compound.
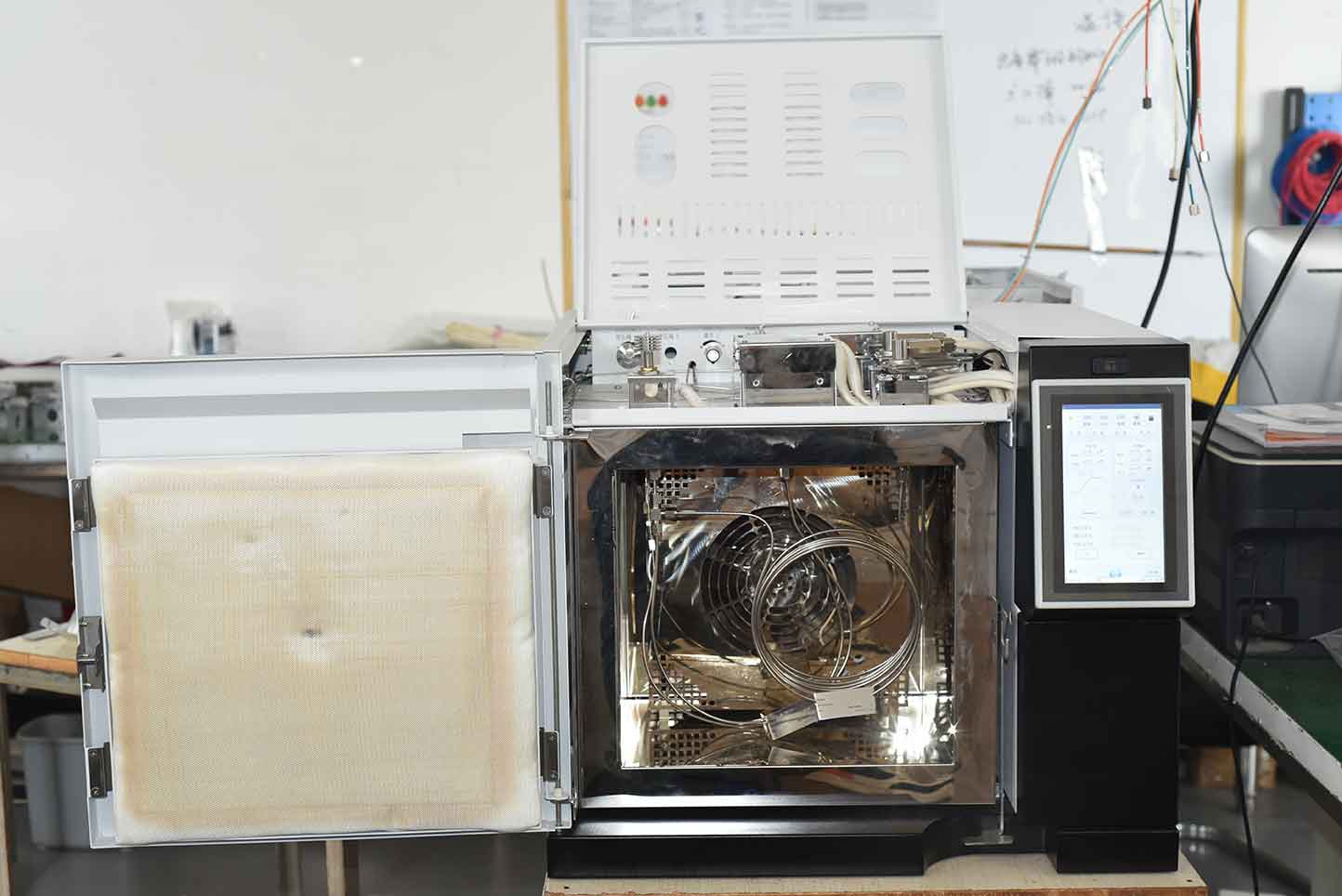

ZC-215 insulation oil gas chromatography analyzer is a technology for separating and analyzing multi-component mixtures. It mainly utilizes the differences in boiling points, polarity, and adsorption coefficients of each component in the sample in the chromatographic column to separate each component in the column, and conducts qualitative and quantitative analysis of the separated components. This instrument is designed in accordance with the requirements of the "Determination of Dissolved Gas Components in Insulating Oil (Chromatography)" in the power system. It adopts microcomputer automatic control, full keyboard operation, and large screen LCD display. It has the characteristics of high temperature control accuracy, stable and reliable performance, high sensitivity, and good repeatability. The equipment can be used for internal fault detection of oil and gas equipment in the power system, cooling medium analysis of hydrogen cooled generators, sulfur hexafluoride impurity analysis, boiler flue gas analysis, natural gas analysis, and environmental monitoring analysis. It can be used for both specialized analysis and general analysis, making it an effective equipment for gas analysis in petroleum, chemical, mining, and other systems.
Kvtester Electronics Technology Co.,Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise specializing in power testing, testing, research and development, production, and sales of testing equipment. It has been engaged in the electrical testing industry for many years, and its products are of high quality. We welcome customers to come and purchase.