Relay protection tester plays a crucial role in the power system, used to detect and protect the normal operation of power equipment. However, during use, the relay protection tester may encounter various faults. The following is an analysis of common faults and their causes:
1. Power failure
① Fault phenomenon:
The device cannot be turned on normally. The display screen has no display or abnormal display.
② Cause analysis:
Poor contact of power cord: Due to long-term use or improper human operation, the connection between the power cord and the equipment may become loose or have poor contact, thereby affecting the normal power supply of the equipment.
Power adapter failure: The power adapter is an important component of the tester. If its internal circuit is damaged, the output voltage is unstable, etc., it will cause the equipment to be unable to supply power normally.
Insufficient or damaged battery power: Some testers use built-in batteries for power supply. If the battery power is insufficient or damaged, it can also cause the device to not start up properly.
Aging of power lines or blown fuses: Long term high load operation may cause aging of power lines and blown fuses, making the tester unable to function properly.
2. Communication malfunction
① Fault phenomenon:
The communication between the tester and the device under test is not functioning properly.
Test data cannot be transmitted or transmitted incorrectly.
② Cause analysis:
Communication line failure: Poor connection, damaged or excessively long communication lines can all cause signal attenuation or loss, leading to communication failures.
Communication parameter setting error: If the communication parameter settings of the tester and the tested device are inconsistent, such as baud rate, data bits, stop bits, etc., it can also cause communication failures.
Communication interface failure: Communication interface failures between the tester and the device under test, such as loose, damaged, or incompatible interfaces, can also cause communication failures.
3. Abnormal test results
① Fault phenomenon:
The test data is inaccurate.
Test waveform abnormality.
The test results did not meet expectations.
② Cause analysis:
Test parameter setting error: If the test parameters are set incorrectly, such as test current, voltage, frequency, etc., which do not match the actual requirements, it will result in inaccurate test results.
There are problems with the test object: If the tested device itself has faults or abnormalities, such as component damage, short circuits or open circuits, it can also cause abnormal test results.
Test environment interference: Electromagnetic interference, temperature, humidity, and other factors in the test environment may also affect the test results, leading to abnormal test results.
4. Test channel abnormality
① Fault phenomenon:
The testing channel is not functioning properly.
The test results are unstable or cannot be reproduced.
② Cause analysis:
Loose or damaged test card: The test card is an important component of the test channel, and if it is loose or damaged, it will directly affect the normal operation of the test channel.
Poor wiring contact: If the wiring in the test channel is poorly connected, it can cause poor signal transmission, thereby affecting the test results.
Damaged collection board: The collection board is responsible for collecting test data. If it is damaged, it will result in the inability to correctly collect and process test data.
5. Host hardware malfunction
① Fault phenomenon:
The tester is not functioning properly.
The display screen is unresponsive or displaying abnormally.
② Cause analysis:
CPU failure: The CPU is the core component of the tester, and if it fails, it will directly cause the tester to malfunction.
Memory failure: Memory issues may cause abnormal program operation or data loss, thereby affecting the normal operation of the tester.
Hard drive failure: Hard drive damage may result in data being unable to be saved or read, thereby affecting the testing results and data processing capabilities of the tester.
6. Software malfunction
① Fault phenomenon:
The software is running abnormally.
The program crashed.
Data exception.
② Cause analysis:
Software defects: Software may have defects during development or upgrade, resulting in unstable operation or functional failure.
Virus infection: If the device is attacked by a virus, it may cause abnormal software operation or software functionality failure.
Human error: If the operator accidentally deletes or modifies key files or settings during use, it may also cause software failure.
In summary, common faults of relay protection testers involve multiple aspects such as power supply, communication, test results, test channels, host hardware, and software. In order to ensure the normal operation of the tester and the accuracy of the test results, it is necessary to regularly maintain and inspect the tester, promptly detect and handle faults.
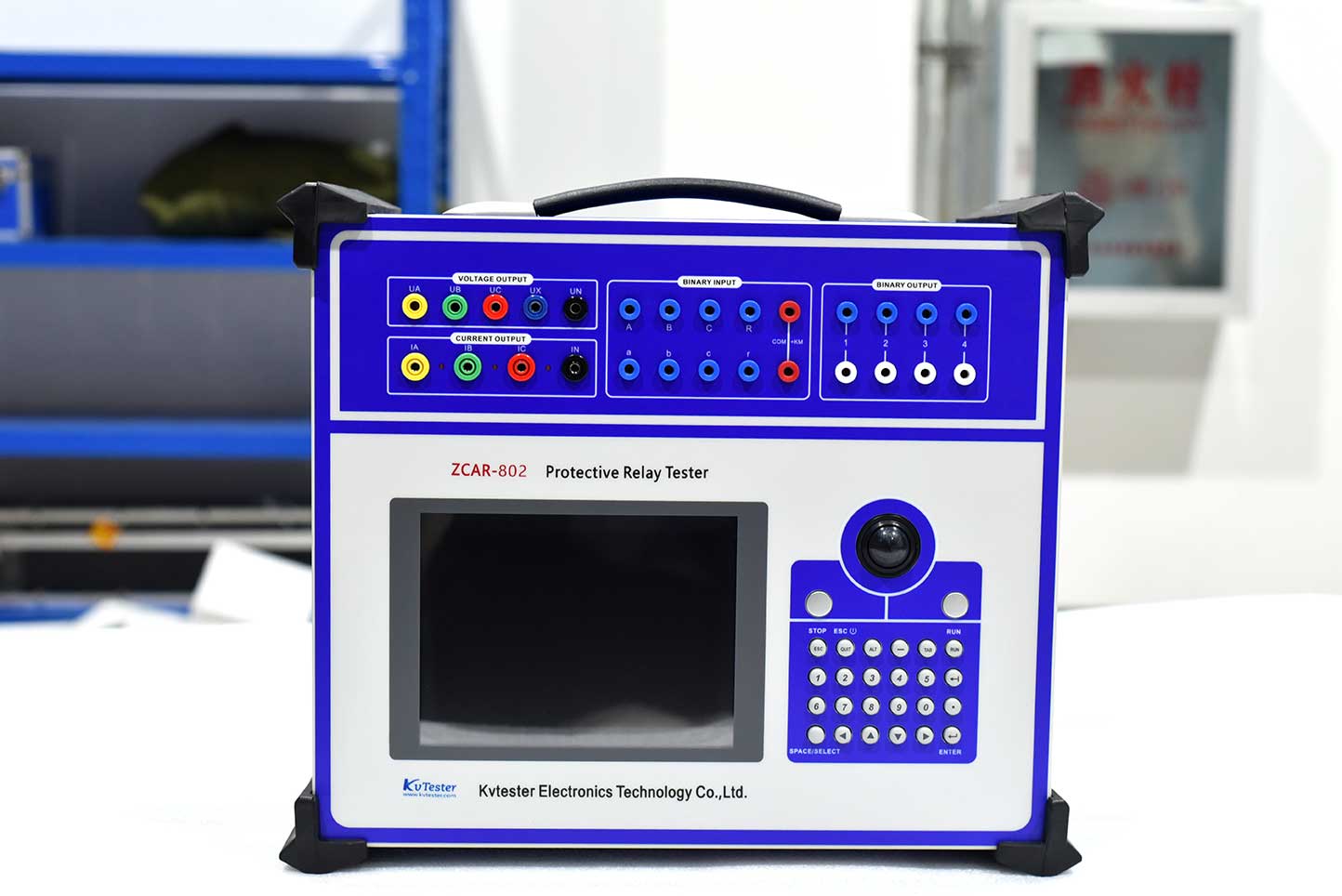

ZCAR-802 microcomputer relay protection tester is an important test tool to ensure the safety and reliability of power system operation.adopted modern latest new digital technology, high precision electronic parts, micro system with new circuits and new structure.It Can independently complete test of microcomputer protection, relay protection, excitation, measurement, fault recording and other professional fields tests, widely used in electric power, petrochemical, metallurgy, railway, aviation, military and other industries of scientific research, production and electrical test site.
Kvtester Electronics Technology Co.,Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise specializing in power testing, testing, research and development, production, and sales of testing equipment. It has been engaged in the electrical testing industry for many years, and its products are of high quality. We welcome customers to come and purchase. Service hotline: 0086-27-81778799, to learn more, visit the official website: www.kvtester.com