The digital partial discharge detector, as a key tool for evaluating the insulation status of high-voltage electrical equipment, has a wide range of application scenarios covering the full lifecycle management of power equipment, including manufacturing, operation, maintenance, and scientific research. The following is a detailed explanation of its core application scenarios:
1. Equipment manufacturing and factory testing
① Transformer manufacturing
Application scenario: In the manufacturing process of transformer windings, insulation cardboard, oil immersed insulation and other components, detecting partial discharge to verify the uniformity and process quality of insulation materials.
Purpose of testing: To avoid post factory failures caused by insulation defects (such as air gaps and impurities) and ensure that the product complies with international standards (such as IEC 60076, GB/T 1094).
② High voltage cable production
Application scenario: Conduct partial discharge testing on the insulation layer of cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) cables to check if the extrusion process introduces defects.
Purpose of testing: To prevent tree like breakdown (electrical branches) caused by partial discharge during cable operation and extend its service life.
Method: The oscillation wave voltage method (OWTS) or ultra-low frequency (0.1Hz) voltage method is used to simulate actual operating conditions for detection.
③ Assembly of switchgear (GIS/GIL)
Application scenario: During the assembly process of gas insulated metal enclosed switchgear (GIS) or gas insulated transmission lines (GIL), detect partial discharge at the connection of pot insulators and conductors.
Purpose of testing: To ensure sealing and insulation performance, and avoid accidents caused by SF6 gas leakage or insulator surface discharge during operation.
2. On site operation equipment testing
① Regular inspections and preventive maintenance
Application scenario: Regular partial discharge detection of transformers, cables, switches and other equipment in operation to detect early signs of insulation degradation.
Detection purpose: To predict the development of faults and avoid sudden power outages through trend analysis (such as changes in discharge capacity over time).
② Fault diagnosis and localization
Application scenario: When the device encounters abnormalities (such as oil chromatography analysis abnormalities, infrared thermal imaging abnormalities), combined with partial discharge detection to locate the fault point.
Purpose of testing: To quickly determine the type and location of discharge (such as air gap discharge, surface discharge) and guide maintenance strategies.
③ Acceptance after major overhaul
Application scenario: After equipment overhaul (such as transformer core maintenance, cable joint replacement), the maintenance quality is verified through partial discharge detection.
Purpose of testing: To ensure that repairs do not introduce new defects and avoid repeated failures.
Standard: Referring to IEC 60270 or GB/T 7354, the discharge capacity should be lower than the allowable threshold of the equipment (such as transformer<100pC).
3. Online monitoring and smart grid
① Transformer online monitoring
Application scenario: Install partial discharge sensors at transformer oil tanks or bushings to monitor insulation status in real-time.
technology
Ultrasonic method: detecting the sound waves generated by discharge through piezoelectric sensors, suitable for outdoor transformers.
Ultra high frequency method (UHF): detects electromagnetic waves generated by discharge (300MHz~3GHz), with strong anti-interference ability.
System integration: Integrate with oil chromatography, infrared monitoring and other data to build a transformer condition evaluation platform.
② Cable online monitoring
Application scenario: Install high-frequency current sensors (HFCT) at cable joints or terminals to monitor partial discharge signals.
technology
Distributed fiber optic sensing: Lay fiber optic cables along the cable and locate discharge points by detecting changes in backscattered light.
Wireless sensor network: Low power design, suitable for long-distance cable monitoring.
Advantages: Real time warning, reducing manual inspection costs.
③ Online monitoring of switchgear (GIS)
Application scenario: Install UHF sensors at GIS bowl insulators or conductor connections to monitor partial discharge.
technology
Phase resolved pulse sequence analysis (PRPSA): Determine the type of fault based on the temporal characteristics of discharge pulses.
Machine learning algorithms: Train models on historical data to achieve automatic fault classification (such as metal particle discharge, floating potential discharge).
4. Research and Teaching Applications
① Research on Insulation Materials
Application scenario: Simulate the partial discharge characteristics of new insulation materials (such as nanocomposites) under different voltage and temperature conditions in the laboratory.
Purpose: To evaluate the ability of materials to resist partial discharge and optimize formula design.
② Fault simulation experiment
Application scenario: Simulate partial discharge through artificial defect models (such as air gaps and metal tips) to study the mechanism of discharge development.
Method: Combining high-speed cameras, infrared thermal imagers, and other multi physics field synchronous observations, analyze the correlation between discharge and heat, sound, and light.
③ Teaching and Training
Application scenario: In university or power enterprise training, use partial discharge detectors to demonstrate discharge phenomena and detection methods.
Tool: Portable detector paired with simulated fault device to help students master operational skills and data analysis.
summary
The application scenario of digital partial discharge detector runs through the entire process of power equipment from manufacturing to retirement, and its core value lies in achieving early warning and accurate diagnosis of insulation status through non-destructive detection. With the development of smart grid and IoT technology, detectors are evolving from offline testing to online monitoring, and from single parameter to multi physical field fusion, providing stronger technical support for the safe operation of power equipment.
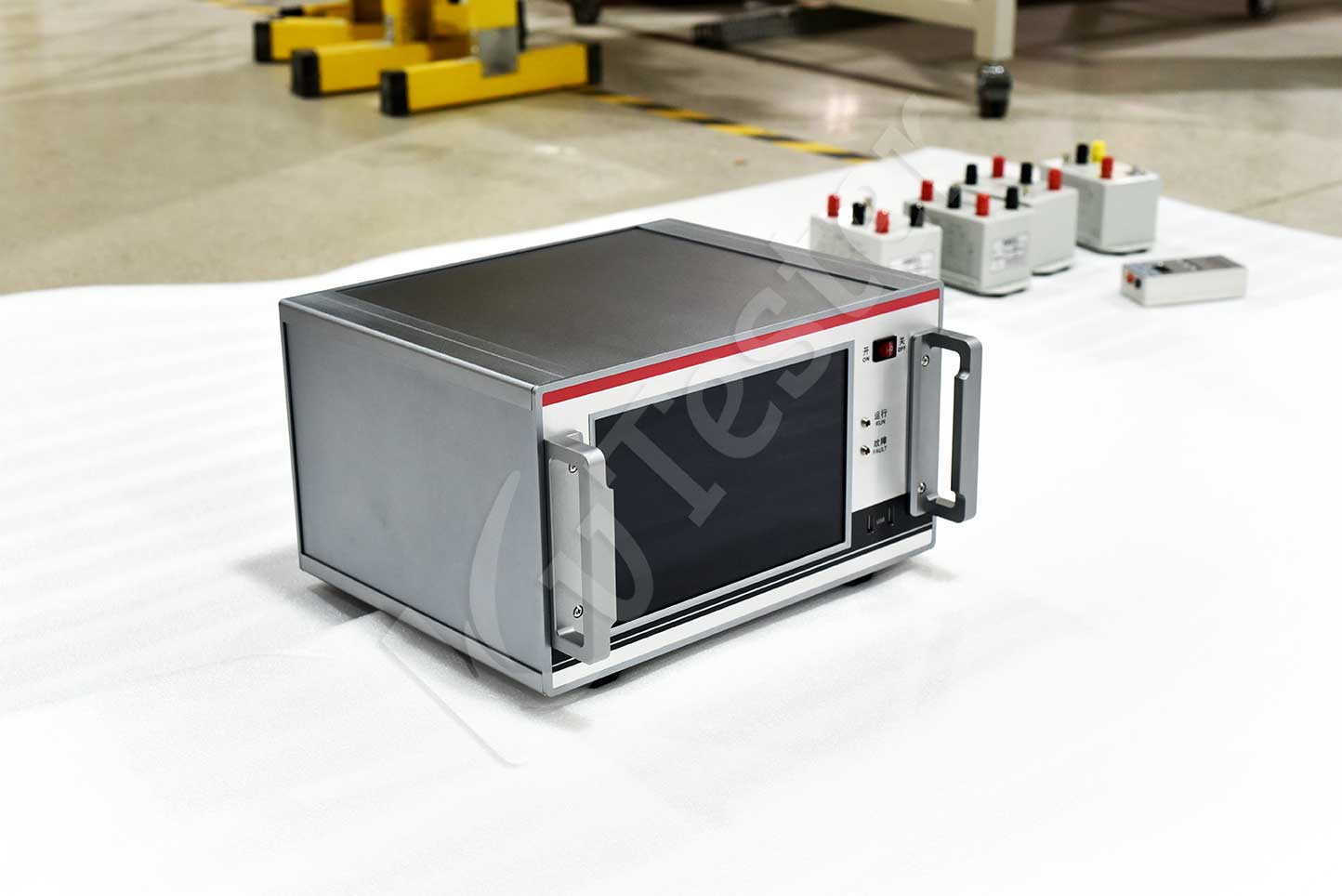

ZC-254-IV digital partial discharge detector adopts an integrated machine design, which is easy to operate. This instrument is suitable for type testing, factory testing, and handover testing of high-voltage products, and can complete quantitative testing of partial discharge of motors, transformers, cables, bushings, capacitors, transformers, lightning arresters, switches, and other high-voltage electrical appliances.
Kvtester Electronics Technology Co.,Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise specializing in power testing, testing, research and development, production, and sales of testing equipment. It has been engaged in the electrical testing industry for many years, and its products are of high quality. We welcome customers to come and purchase. Service hotline: 0086-27-81778799, to learn more, visit the official website: www.kvtester.com