Internal resistance testing of batteries is a crucial step in assessing their health, predicting remaining lifespan, and preventing failures. Internal resistance testing measures the internal resistance value of the battery, reflecting problems such as aging of battery plates, electrolyte drying, or loose connections. The following are detailed testing steps, method selection, and precautions to help you efficiently complete the test and accurately interpret the results.
1. Pre-test Preparation: Ensure Conditions and Equipment are Ready
① Select Appropriate Testing Equipment
Type Selection:
Portable internal resistance tester: Suitable for quick on-site testing, supporting single-cell or multi-cell battery testing (e.g., 2V, 6V, 12V).
Online monitoring system: Suitable for data centers, substations, and other scenarios requiring long-term monitoring, capable of real-time acquisition of internal resistance data.
High-precision laboratory equipment: Used for battery research and development or in-depth fault analysis, supporting micro-ohm level measurement (e.g., 0.001mΩ accuracy).
Function Matching:
Confirm that the equipment supports the voltage range of the battery under test (e.g., a 48V system requires a 0-60V range).
Prioritize equipment with data storage, trend analysis, or Bluetooth/Wi-Fi transmission capabilities for easier subsequent management.
② Check Battery Status
Visual Inspection:
Observe whether the battery casing is bulging, leaking, or has corroded terminals. These problems will directly affect the internal resistance test results.
Case example: A battery in a communication base station had oxidized terminals due to leakage, resulting in increased contact resistance during testing and a 30% artificially high internal resistance value.
Voltage Pre-check:
Use a multimeter to measure the open-circuit voltage of the battery to ensure it is within the normal range (e.g., a 12V battery voltage should be between 10.8V and 14.4V).
Note: Under-voltage or over-voltage batteries may damage the tester; they need to be charged or discharged to a safe voltage first.
③ Environmental Condition Control
Temperature: Test in an environment of 15℃-35℃ (some equipment supports -10℃ to 50℃), avoiding temperature effects on sensor accuracy.
Humidity: Relative humidity <85%, to prevent condensation or short circuits inside the equipment.
Electromagnetic Interference: Keep away from strong interference sources such as chargers and inverters, or choose anti-interference equipment (e.g., models using spectral analysis algorithms). 2. Test Method Selection: Matching Technology to the Scenario
① AC Injection Method (Recommended for Online Testing)
Principle: A small-amplitude AC signal (e.g., 1kHz frequency) is injected into the battery, and the internal resistance is calculated by measuring the phase difference between voltage and current.
Steps:
Connect the current probe of the tester to the negative terminal of the battery and the voltage probe to the positive terminal.
Start the test; the device automatically injects the AC signal and calculates the internal resistance value.
Record the data and compare it with the baseline value (e.g., factory internal resistance or historical test values).
Advantages: No need to disconnect the battery connection, suitable for online monitoring; fast test speed (single cell <3 seconds).
Limitations: Sensitive to high-frequency noise, requiring anti-interference design.
② DC High Current Method (Suitable for Offline Testing)
Principle: By briefly discharging with a large current (e.g., 10A pulse), the voltage drop is measured to calculate the internal resistance (formula: R=ΔV/ΔI).
Steps:
Disconnect the battery load and connect the discharge circuit of the tester.
Start the test; the device applies a short-duration pulse current and records the voltage change.
Calculate the internal resistance value according to the formula.
Advantages: Intuitive results, suitable for laboratory or offline scenarios.
Limitations: Requires disconnecting the battery connection, which may cause a brief power outage; the pulse width should be <10ms to avoid battery overheating.
③ Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS, Advanced Analysis)
Principle: By scanning AC signals at different frequencies, an impedance spectrum is plotted to analyze the internal electrochemical processes of the battery.
Steps:
Connect the battery using a professional EIS tester.
Set the frequency range (e.g., 0.01Hz-10kHz), automatically scan and generate the impedance spectrum.
Fit the data using an equivalent circuit model to obtain parameters such as internal resistance and diffusion resistance.
Advantages: Can distinguish between ohmic internal resistance and polarization internal resistance, allowing for in-depth analysis of aging mechanisms.
Limitations: Expensive equipment, complex operation, suitable for R&D or fault diagnosis scenarios.
3. Test Operation Procedure: Standardized Steps to Reduce Errors
① Connecting the Test Equipment
Kelvin Test Clips: Use four-terminal test clips to ensure that the current loop and voltage sampling loop are separated, reducing the impact of contact resistance.
Clamping Force: Apply even pressure (recommended 5N-10N) to avoid deformation of the terminals or poor contact. Case Study: A car repair shop used ordinary alligator clips for testing, resulting in unstable contact resistance and a ±15% fluctuation in internal resistance measurements.
② Start testing and record data
Single-cell testing: Test each battery cell sequentially, recording the internal resistance value, voltage, and test time.
Group testing: Test the entire battery pack to assess consistency within the group (calculate standard deviation or dispersion).
Data storage: Use the device's built-in storage or export the data to a computer to create a battery health record.
③ Repeat testing to verify results
Multiple measurements: Perform three tests on the same battery and take the average to reduce random errors.
Comparative verification: If the results differ by more than 5%, check the connection or equipment status and retest.
4. Result Interpretation and Subsequent Actions: From Data to Decision
① Baseline comparison
Factory values: Refer to the battery's factory internal resistance data; if the current value exceeds the factory value by more than 20%, it requires close attention.
Industry standards: For example, IEEE 1188-2018 stipulates that valve-regulated lead-acid batteries with an annual internal resistance increase rate of >10% require maintenance.
Historical trends: Analyze the internal resistance growth rate based on long-term test data (e.g., a monthly increase of 0.5% is considered normal).
② Anomaly handling suggestions
Single-cell internal resistance exceeding the limit:
Perform a deep discharge test to confirm whether the capacity meets the standard (if the capacity is <80%, replacement is recommended).
Check if the terminal connections are loose, retighten them, and retest.
High dispersion within the group:
Perform equalization charging on the battery pack to improve consistency.
If the dispersion is >15%, consider adjusting the grouping or replacing some batteries.
③ Trend warning settings
Threshold alarm: Set an internal resistance threshold (e.g., trigger maintenance when the lead-acid battery exceeds the limit by 20%).
Life prediction: Predict the remaining battery life based on the internal resistance growth model (e.g., Arrhenius equation).
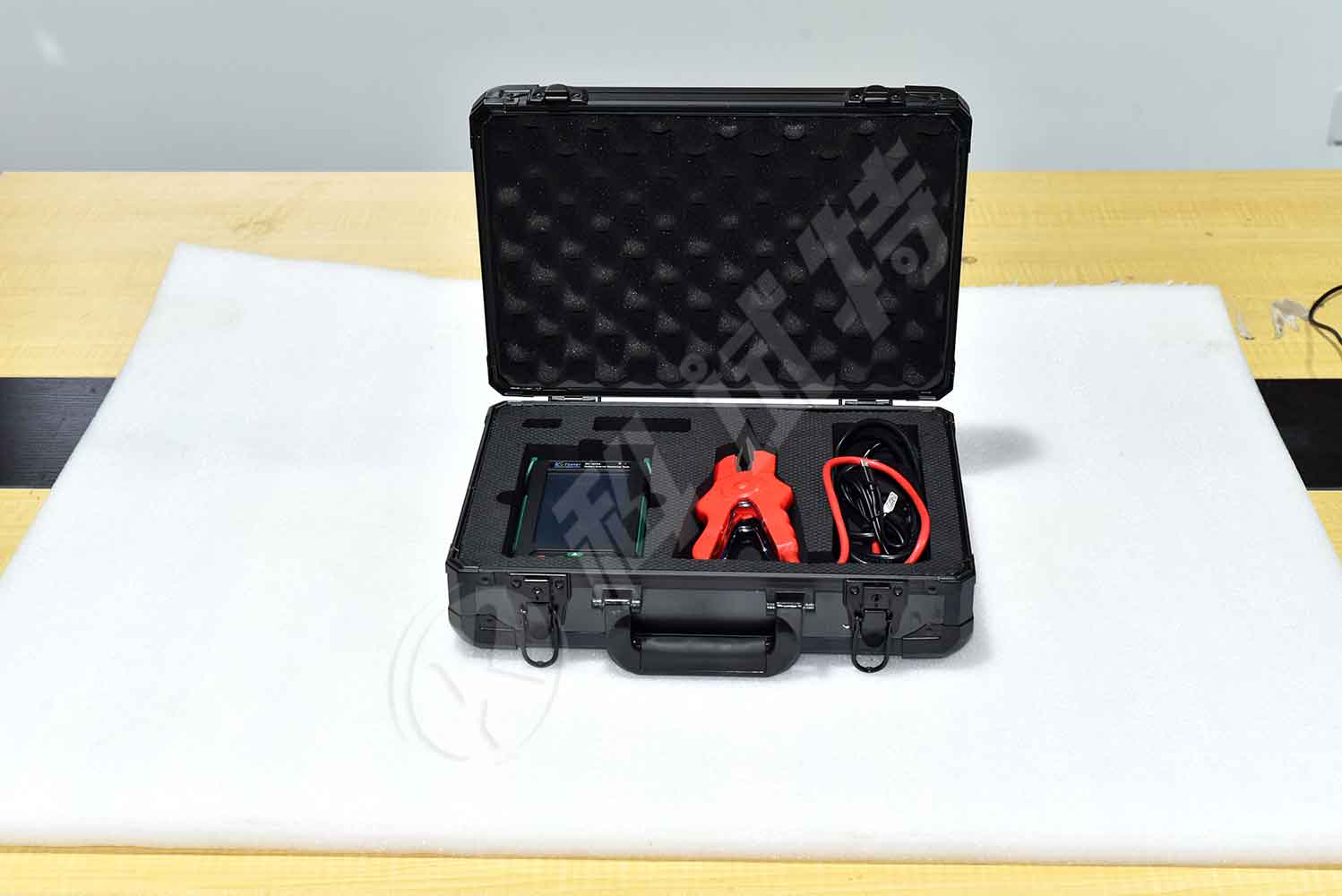

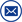
ZC-422A Battery Internal Resistance Tester is designed using the advanced AC discharge measurement method to test voltage, resistance and conduct of cell battery online. It can store , process the detected data and alarm the battery failure. The tester can accurately and effectively discern the condition of cell battery. The instrument saves, queries, deletes and exports the test data. The upper computer software analyzes and displays the test data through various charts and graphs . It automatically generates the battery test report.
Kvtester Electronics Technology Co.,Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise specializing in power testing, testing, research and development, production, and sales of testing equipment. It has been engaged in the electrical testing industry for many years, and its products are of high quality. We welcome customers to come and purchase. Service hotline: 0086-27-81778799, to learn more, visit the official website: www.kvtester.com