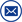
ZC-610A digital double clamp phase voltammeter is a kind of high precision, low price, hand-held, dual channel input measuring instrument designed for on-site measurement of voltage, current and phase. It is convenient to measure the phase between U-U, I-I and U-I, distinguish the phase sequence of inductive circuit, capacitive circuit and three-phase voltage, detect the connection group of transformer, test the secondary circuit and bus differential protection system, read out the phase relationship between CT of differential protection groups, and check whether the wiring of Watt hour meter is correct. The clamp current transformer is used to input the measured current, so there is no need to disconnect the measured line. When measuring the phase between U1 and U2, the two input circuits are completely insulated and isolated, so it can completely avoid the short circuit of the measured line caused by the possible wrong wiring, which may lead to the burning of the measuring instrument. The display adopts high contrast liquid crystal display, the word is up to 25 mm, and the screen angle can be freely changed about 70 ° to obtain the best visual sight.

Press the on-off button and rotate the functional range switch to select the test parameters and limits correctly.
1. Measuring AC voltage
Turn the function range switch to the 500V limit corresponding to parameter U1, and input the measured voltage from U1 jack to measure. If the measured value is less than 200V, the switch can be directly rotated to 200V limit measurement corresponding to U1 to improve the measurement accuracy.
The two channels have the same voltage test characteristics, so the switch can be turned to the corresponding limit of parameter U2 to measure the measured voltage from the U2 jack input.
2. Measuring AC current
Turn the rotary switch to the 10A limit corresponding to parameter I1, insert the outlet plug of secondary side of clamp current transformer with label I1 into I1 jack, and clamp the jaw on the measured line to conduct measurement. Similarly, if the measurement value is less than 2A, the switch can be directly rotated to the 2A limit measurement corresponding to I1 to improve the measurement accuracy.
When measuring the current, the rotary switch can also be turned to the limit corresponding to the parameter I2, and the measuring clamp labeled I2 is connected to the I2 jack, and the jaw of the clamp is clamped on the measured circuit for measurement.
3. Measure the phase angle between the two voltages
When measuring the phase angle of U2 lagging U1, turn the switch to parameter U1U2. During the measurement process, the switch can be turned clockwise to each limit of parameter U1 to measure the input voltage of U1, or the switch can be turned anticlockwise to each limit of parameter U2 to measure the input voltage of U2.
Note: during phase measurement, the symbols U1 and U2 beside the voltage input jack and the red "*" symbol of the clamp current transformer are the terminals with the same phase name.
4. Measure the phase angle between the two currents
When measuring the phase angle of I2 lagging I1, turn the switch to parameter I1I2. Similarly, during the measurement process, the input current of I1 can be measured by turning the switch clockwise to each limit of parameter I1, or the input current of I2 can be measured by turning the switch anticlockwise to each limit of parameter I2.
5. Measure the phase angle between voltage and current
Input the voltage from U1, input the current from I2 with I2 measuring clamp, rotate the switch to parameter U1I2, and measure the angle of current hysteresis voltage. During the test, the switch can be turned clockwise to measure current at each limit of parameter I2, or anticlockwise to measure voltage of parameter U1.
The voltage can also be input from U2, the current is input from I1 with I1 measuring clamp, and the switch is rotated to parameter I1U2 position to measure the angle of voltage hysteresis current. In the same way, the switch can be rotated at any time to measure the value of I1 or U2.
6. Phase sequence discrimination of three phase three wire distribution system
Turn the switch to U1U2 position. Connect phase a of three-phase three wire system to U1 jack, B-phase to ± jack corresponding to U1 and ± jack corresponding to U2, and c-phase to U2 Jack. If the measured phase value is about 300 °, at this time, the measured system is in positive phase sequence; if the measured phase is about 60 °, the measured system is in negative phase sequence.
To change a measurement method, connect phase a to U1 jack, B phase to ± Jack and U2 socket corresponding to U1, and C phase to ± jack corresponding to U2. At this time, if the measured phase value is 120 °, it is positive phase sequence; if the measured phase value is 240 °, it is negative phase sequence.
7. Phase sequence discrimination of three phase four wire system
Turn the switch to U1U2 position. Connect a phase to U1 jack, B phase to U2 jack, and connect zero line to ± jack of two input circuits at the same time. If the phase is about 120 ° it is positive phase sequence; if it is 240 ° or so, it is negative phase sequence.
8. Discrimination of inductive and capacitive loads
Turn the switch to U1I2 position. The load voltage is connected to U1 input terminal, and the load current is connected to I2 jack through measuring clamp. If the phase is displayed in the range of 0 ° to 90 ° the measured load is inductive; if the phase is displayed in the range of 270 ° to 360 ° the measured load is capacitive.