AC and DC withstand voltage tests are two core methods in electrical insulation performance testing, and they have significant differences in principles, application scenarios, advantages, and disadvantages. The following is a detailed comparative analysis:
1. Differences in Core Principles
① AC Withstand Voltage Test
Principle: Applying a sinusoidal AC voltage to simulate the power frequency or high-frequency voltage environment during the actual operation of the equipment.
Voltage Characteristics: The voltage direction changes periodically, generating an alternating electric field, testing the insulation material's ability to withstand dynamic electric fields.
Typical Waveform: Standard sine wave (50Hz/60Hz).
② DC Withstand Voltage Test
Principle: Applying a constant DC voltage to test the breakdown strength of the insulation material under a static electric field.
Voltage Characteristics: The voltage direction is constant, and the electric field distribution is determined by the resistivity of the insulation material, making it easy to detect local defects.
Typical Waveform: Constant DC voltage.
2. Comparison of Application Scenarios
| Scenario | AC withstand voltage test | DC withstand voltage test |
| Electrical equipment | Transformers, cables, switchgear, etc. | Cables, capacitors, motor windings, etc. |
| Insulating material | Solid insulation | Liquid/solid insulation |
| Preventive testing | Regularly inspect equipment for insulation aging | Detection of partial discharge or insulation weaknesses |
| Research and development phase | Verifying the pressure resistance level of the equipment design | Evaluating the insulation performance of new materials |
3. Advantages and Disadvantages Analysis
① AC Withstand Voltage Test
Advantages:
Closely simulates actual operating conditions, mimicking real-world scenarios such as power frequency overvoltage and switching overvoltage.
Can detect the comprehensive performance of insulating materials under alternating electric fields, such as dielectric loss and partial discharge.
Disadvantages:
High test voltage and large equipment capacity result in higher costs.
Weak ability to locate insulation defects, potentially masking localized problems.
Repeated testing may accelerate insulation aging (e.g., shortened lifespan of cables after multiple AC withstand voltage tests).
② DC Withstand Voltage Test
Advantages:
a.Simple and low-cost test equipment, suitable for rapid on-site testing.
b.Sensitive to localized defects (such as bubbles and cracks), making it easy to detect early faults.
c.The voltage can be gradually increased, facilitating observation of signs before insulation breakdown.
Disadvantages:
a.Unable to simulate dielectric loss and thermal effects under alternating electric fields.
b.Uneven electric field distribution inside the insulation under DC voltage (e.g., electric field concentration in oil-impregnated paper insulation), potentially underestimating the actual risk.
c.DC withstand voltage testing of AC equipment (such as transformers) may generate residual charges, requiring sufficient discharge.
4. Practical Application Suggestions
① Prioritize AC withstand voltage testing:
For overall insulation assessment of AC equipment (such as transformers and cables).
To simulate operating overvoltage or lightning overvoltage scenarios.
② Prioritize DC withstand voltage testing:
To detect defects in DC equipment (such as capacitors and DC cables) or localized defects.
For quick on-site screening of insulation problems (such as motor windings).
③ Combined use:
First, use DC withstand voltage testing to locate localized defects, and then use AC withstand voltage testing to verify overall performance.
For important equipment (such as ultra-high voltage cables), use a combined approach of "DC pre-testing + AC withstand voltage testing".
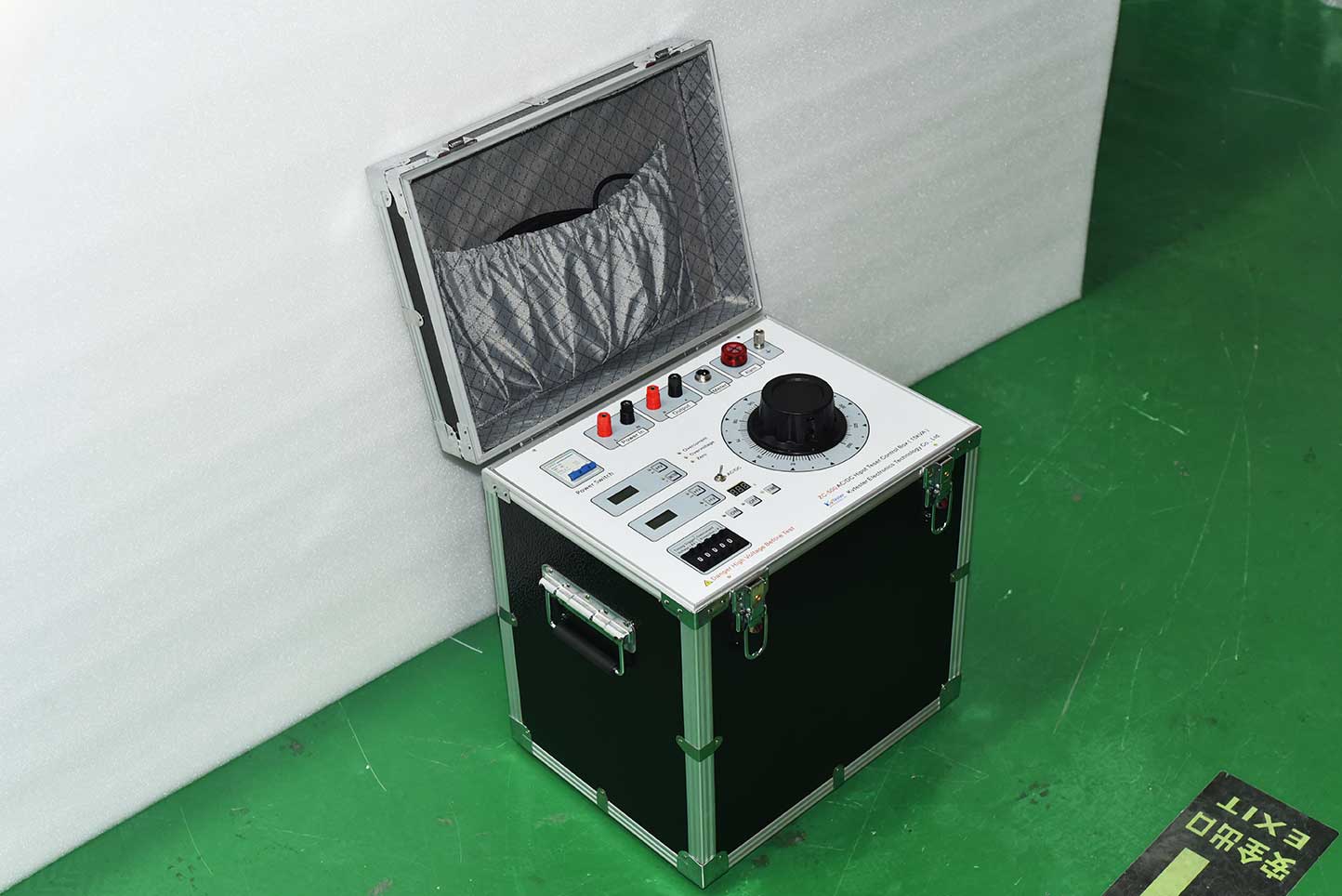

ZC-500 power-frequency voltage-resistant control box adopts CNC technology and has strong anti-interference ability. Compared with the previous generation of operation box, it has the characteristics of small size, light weight and beautiful appearance. Its output voltage amplitude is continuously adjustable from 0 to 250V, which is used for voltage regulation control of calibration, detection and test equipment. The operation box is simple, compact, firm, reliable and easy to maintain. It is an ideal control equipment for outdoor high-voltage test and can be widely used in electric power, water conservancy, chemical industry, railway and other industries and laboratories.
Kvtester Electronics Technology Co.,Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise specializing in power testing, testing, research and development, production, and sales of testing equipment. It has been engaged in the electrical testing industry for many years, and its products are of high quality. We welcome customers to come and purchase. Service hotline: 0086-27-81778799, to learn more, visit the official website: www.kvtester.com